Selecting New Stainless Steels for Unique Applications
Technical Guide
Abstract
For many years, material specifiers have had to deal with the uncertainty of selecting the "right" stainless steel for a given application. More recently, new technologies in the manufacture of stainless steels and new performance requirements have fostered a series of new stainless alloys with unique properties and characteristics. This presentation will discuss these new materials and show how they relate to the more common stainless steels, in the important selection process.
Introduction
Technological advances in materials over the past decade present interesting challenges today for the designers and manufacturers of the products spawned by these advances. Among these challenges is how to select the "best" material for finished components and the equipment used to manufacture a wide variety of end-use products.
Typically, the selection of a stainless steel has been made based on corrosion resistance and/or strength. In general, the selection process has started with the popular 304 stainless. If more or less corrosion resistance is required, one moves up to an alloy like 316 stainless or down to an alloy like 405 stainless. If more strength is required one might move from 405 stainless to 420 stainless.
The relationship between corrosion resistance and strength for the common stainless steels is shown on the Selectaloy® diagram, figure 1.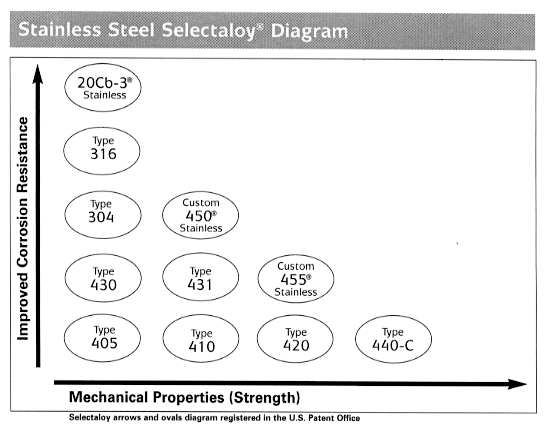
Fig. 1 - stainless steel Selectaloy Diagram.
While corrosion resistance and strength requirements are most frequently considered in choosing a specific stainless steel, they are only two of the five criteria that should be weighed in the selection process. The five criteria are:
- Corrosion Resistance - environment and type of corrosion resistance
- Mechanical Properties - strength, ductility, hardness
- Physical Properties - density, magnetic properties
- Fabrication - machining, cold forming, welding
- Final Component Cost - material cost, fabrication cost, component life cycle, replacement costs
New Stainless Steels
The technologies used in the manufacturing of stainless steels have improved dramatically over the past several decades. They include refined melting technologies, powder metallurgical billet technology, improved hot working and heat treating technologies and equipment.
We will discuss five new stainless steels, introduced over the past several years, that rely on the new technologies for successful processing. Their compositions are shown in figure 2, their unique properties in figure 3, and their relationship to the conventional stainless steels are demonstrated graphically in figure 4.
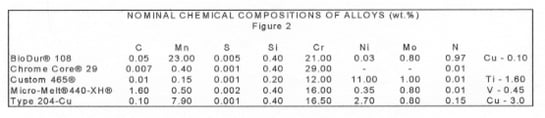
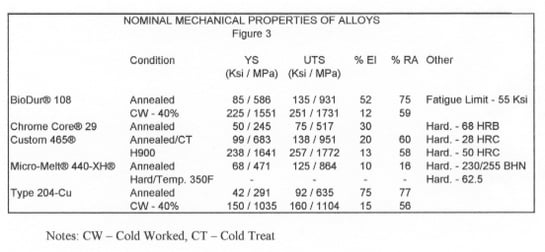
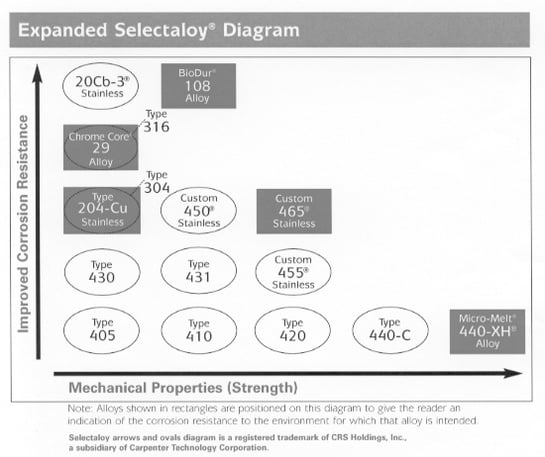
Fig. 4 - relationship of five new stainless steels to conventional stainless steels.
BioDur® 108 is a new fully austenitic alloy with less than 0.05% nickel. This alloy has been designed to have corrosion resistance and mechanical properties equal to or superior to BioDur® 22Cr-13Ni-5Mn or BioDur® 734 Stainless. The alloy was developed in response to concerns over nickel toxicity by the European medical community.
Bio-compatibility testing, including: cytotoxicity, irritation, acute systemic toxicity and pyrogenicity tests indicate that BioDur® 108 may be considered for implanted medical devices.
High nitrogen content, possible through unique melting technology, allows this alloy to be cold worked to high levels of tensile, with exceptional ductility and fatigue strength compared with other alloys in the BioDur® family such as 316LS, 22Cr-13Ni-5Mn alloy and BioDur® 734. The resistance of BioDur® 108 to pitting and crevice corrosion is superior to 316LS alloy and equal to that of the 22Cr-13Ni-5Mn.
BioDur® 108 should be considered for use in applications requiring high levels of strength and corrosion resistance. Candidate applications include implanted orthopedic devices such as bone plates, bone screws, spinal fixation components, hip and knee components, hypoallergenic jewelry, orthodontic appliances and other medical components/instruments fabricated by forging and machining.
Chrome Core® 29 Solenoid Quality stainless - is a new soft magnetic ferritic material that has been designed for use in more corrosive environments than those tolerated by 430 stainless. This alloy was developed in response to an expressed need for a magnetic, corrosion resistant alloy with good micro-cleanliness for use in solenoid components.
Its corrosion resistance is significantly better than that of other solenoid quality stainless steels. When tested in accordance with ASTM G150, the alloy exhibited a critical pitting temperature of 14.8°C. The common solenoid stainless steels, like 430FR, typically exhibit critical pitting temperatures of 4 to 6°C. This alloy's low nonmetallic inclusion content, achievable through vacuum melting technology, makes it a candidate material for components that require a very low surface imperfection level and electropolishing.
Chrome Core 29 generally exhibits magnetic properties similar to the other common solenoid grades of stainless steel, i.e. low coercive force and moderate permeability.
This alloy provides high resistivity, similar to that of 430FR Solenoid Quality stainless. This characteristic is beneficial in applications involving AC excitation due to the suppression of eddy current losses.
Electronic components used in severely corrosive environments, such as solenoid valves, are typical of the applications in which CarTech Chrome Core 29 might be used.
Custom 465® stainless - is a new premium-melted, martensitic, age hardenable alloy capable of about 260 Ksi ultimate tensile strength when peak aged. The alloy was designed to have excellent notch tensile strength and fracture toughness in this condition. Custom 465® stainless was developed as a lower cost alternative to nickel base alloys for fasteners, with stress corrosion cracking resistance superior to the commonly used high strength alloy steels used in the aerospace industry. Custom 465® stainless offers the highest combination of strength, toughness and corrosion resistance available in a stainless steel today.
The success in achieving the superior properties exhibited by Custom 465® stainless is based on achieving very low levels of residual elements through specialized melting technology. Overaging provides a superior combination of strength, toughness and stress corrosion cracking resistance compared with other high strength PH stainless alloys such as Custom 455® stainless.
This alloy can be considered for medical instruments requiring high torque and instruments for clamping, spreading and impacting. It can be considered also for a variety of aerospace applications including aircraft landing gear, engine mounts, flap tracks, actuators, tail hooks and other structural components. Other candidate applications include shafting subject to heavy stress, bolts, fasteners and other parts requiring an exceptional combination of high strength, toughness and corrosion resistance.
Micro-Melt® 440-XH® - is a martensitic stainless steel that can be described as either a high hardness 440C stainless or a corrosion resistant D2 tool steel. It is capable of being heat treated to a hardness of Rockwell C 64, and has general corrosion resistance similar to 440C stainless. This material was developed in response to a concern with poor wear resistance on bearing shafts used in a corrosive environment.
Micro-Melt® 440-XH® Alloy is manufactured utilizing powder metallurgical billet instead of conventionally cast ingot. This process results in a fine, very uniform dispersion of carbides which in turn allows for more consistent properties and improved fabricability.
Micro-Melt 440-XH Alloy may be considered for applications that require higher hardness than 440C stainless or more corrosion resistance than D2 tool steel. Improved wear resistance and edge retention are distinctive attributes offered by this alloy. Bearing balls, shafts, rollers and races, valve seats, bushings, punches, dies and surgical and dental instruments requiring good edge retention are all potential applications for CarTech Micro-Melt 440-XH Alloy.
204-Cu stainless – is a copper-containing, low nickel, nitrogen-strengthened, austenitic stainless steel. The alloy's corrosion resistance is similar to 304 stainless steel. The economic impact of high, unstable nickel prices was the motivation for the development of this alloy.
The addition of nitrogen gives the new alloy higher annealed strength than 304 stainless. However, the copper addition reduces the work hardening rate. 204-Cu stainless is nonmagnetic in the annealed condition, and remains nonmagnetic after cold working. Cold forming characteristics are superior to the 200 stainless steels and similar to Type 304.
204-Cu stainless should be considered for applications where 304 stainless has been used previously. These have included wire products such as springs, fencing, rope, belting, nails, pole-line, buttress screws and screens.
Summary
Several key factors should be considered in selecting the most suitable stainless steel for any application. First, using the diagram provided, select the level of corrosion resistance required. Second, choose the level of strength needed. Third, consider the type and amount of fabrication necessary; then select the alloy modification which offers the most desirable fabricating characteristics. Do a thorough value analysis, which includes the initial alloy price, the installed cost and the effective life expectancy of the finished product. Finally, determine availability of the preferred alloy from the steel mill, service center, warehouse or supplier to arrive at the most economical and practical choice.
***
By Robert Brown
Carpenter Technology Corporation
Reading, PA
USA